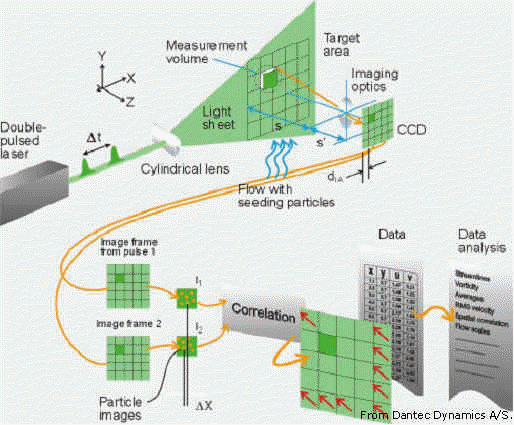
Project Description
Digital PIV System |
||||
|
||||
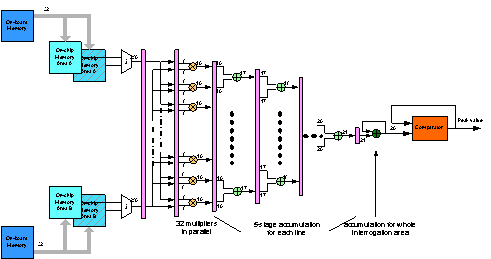
Solution |
||||
|
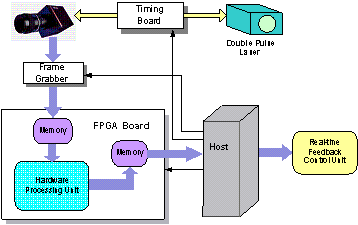
|
|||
|
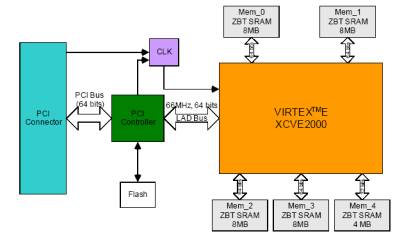 |
|||
|
|
|||
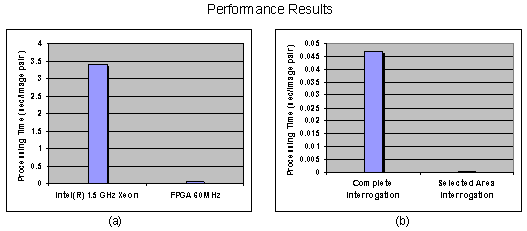
Performance |
||||
|
||||